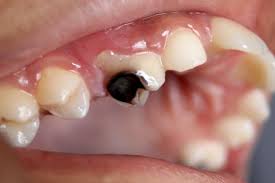
My Child`s Teeth Are Decayed but not Paining -Is Treatment Really Necessary?
Yes, dental treatment is necessary, even when your child’s teeth are decayed but not paining. Many parents feel relieved when their child shows no discomfort, but dental professionals recommend early intervention rather than waiting for pain to develop. Cavities that don’t hurt yet can still progress and cause bigger problems if left untreated.
Understanding Tooth Decay in Children
Tooth decay, also called dental caries or cavities, starts when plaque forming bacteria in the mouth feed on sugars from food and drink and produce acids that weaken the enamel. Over time, this enamel breakdown can create holes or cavities in the tooth. Without treatment, decay can continue deeper into the tooth, eventually reaching the dentin and nerve tissue – the point at which pain typically begins.
Parents searching for “child dental decay early stages no pain” should understand that absence of pain does not mean absence of disease. Cavities often go unnoticed until they have progressed significantly because early decay may not reach the sensitive inner layers of the tooth.
Why Cavities Might Not Cause Pain at First
It’s common for children to have decay that isn’t hurting yet. Pain usually appears only when decay reaches the dentin or nerve centre — which means the cavity has already grown quite large. Because early decay often doesn’t hurt, many parents wonder, “Do I need to treat non painful cavities in kids?” The short answer is yes
Without professional dental care, the decay can continue silently and worsen over time. This makes early detection and treatment crucial to protecting your child’s long term oral health.
Why You Shouldn’t Ignore Non-Painful Tooth Decay
Even if your child isn’t complaining, there are several important reasons why treating cavities before they hurt is essential:
Decay Progresses Without Notice
Cavities can grow deeper and wider over time, eventually reaching the nerve and causing pain, infection and abscesses.
Risk of Pain and Infection Later
If left untreated, a cavity can erupt into a painful infection, affecting your child’s eating, sleep, mood and school performance.
Baby Teeth Affect Permanent Teeth Development
Primary teeth play a critical role in chewing, speaking and guiding permanent teeth into the correct position. Premature loss of baby teeth due to decay can lead to misalignment and orthodontic challenges later.
What Paediatric Dentists Recommend
When children have cavities — even if they are not yet painful — paediatric dentists’ base treatment on factors such as the extent of decay, the child’s age and overall oral health. Common recommendations include:
- Professional fluoride treatments to strengthen enamel and help remineralize early decay.
- Dental fillings to remove decayed tooth material and restore the tooth’s shape and function.
- Dental sealants to protect the chewing surfaces of molars where most cavities start.
- Early restorative options like minimally invasive treatments that prevent decay from advancing.
Modern, Less Invasive Approaches
Innovative treatments like silver diamine fluoride (SDF) can help stop the progression of decay in very early or nonpainful cavities. This treatment is painless, quick, and particularly useful for young children or those who may be anxious about traditional dental procedures.
Preventing Further Tooth Decay
Alongside professional treatment, establishing preventive habits at home can significantly reduce the risk of new decay and help maintain your child’s oral health:
- Brush teeth twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and carefully supervise until the child can brush effectively alone.
- Make regular dental checkups part of your routine — ideally every six months.
- Limit sugary snacks and drinks that feed plaque forming bacteria.
- Consider professional fluoride varnish and sealants as recommended by your dentist.
Note: At Solitaire Family Dentistry, KPHB, we’re committed to helping families understand the importance of timely paediatric dental care and providing compassionate treatment tailored to each child’s needs.
Ready to give your child’s smile the care it deserves?
Call us at +91 62814 97455 to book a consultation at our KPHB clinic and get expert guidance on treating cavities before they cause pain
My Child’s Teeth Are Decayed but Not Paining – Is Treatment Necessary?
(FAQs)
If there is no pain, is treatment still needed?
Yes. Tooth decay can be present without pain and may worsen if left untreated.
Why doesn’t my child feel pain yet?
The decay may not have reached the nerve. Pain usually appears at a later stage
Can milk teeth be ignored since they will fall out?
No. Milk teeth are important for chewing, speech, and guiding permanent teeth.
What happens if decay is not treated?
It can cause infection, pain, swelling, and damage to permanent teeth.
Is early treatment better?
Yes. Early treatment is simpler, less painful, and more affordable.
How can future decay be prevented?
Regular brushing, less sugar, and routine dental check-ups help prevent decay.
