What is The Benefits of Fluoride-
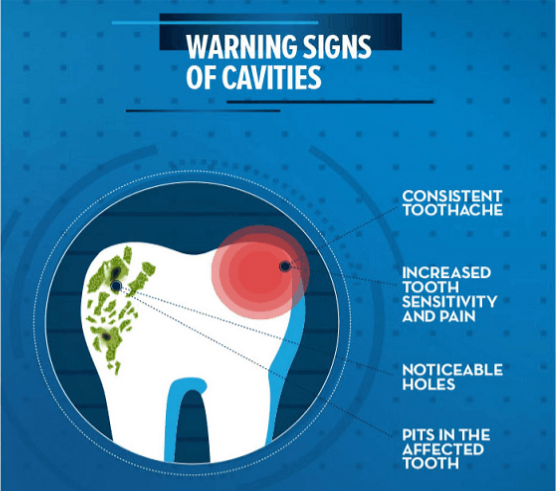
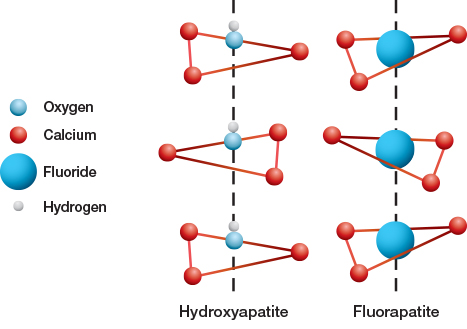
Understanding Fluoride: The Key to Strong and Healthy Teeth The Benefits of Fluoride Prevents tooth decay: Demineralization of teeth is prevented by getting itself incorporated into the enamel mineral, forming Fluorapatite. Fluorapatite is more resistant to acid dissolution than the regular enamel crystal Hydroxyapatites. Strengthens enamel: fluoride works on the partially demineralized subsurface enamel crystals […]
What is The Benefits of Fluoride- Read Post »